Baseball Robots: Throwing, Tracking, Batting, Running, Catching (Thanks to: The University of Tokyo, Baseball Club)
Summary
We have been developing robotic systems that individually achieve fundamental actions of baseball, such as throwing, tracking of the ball, batting, running, and catching. We achieved these tasks by controlling high-speed robots based on real-time visual feedback from high-speed cameras. Before integrating these abilities into one robot, we here summarize the technical elements of each task.
| Throwing: | This robot can throw a ball with high precision using its fingers, similarly to human throwing. To throw a high-speed ball, we proposed a strategy focused on the superposition of wave patterns based on the kinetic chain. This robot can throw the ball into the strike zone with a success rate of 90%. | |
| Tracking: | The AVS, Active Vision System, can achieve a wide field of view by rotating a camera around its pan and tilt axes. Thanks to high-speed actuators and high-speed visual feedback, this system can track a target moving at a high velocity. 1ms Auto Pan/Tilt can track even faster objects by moving two mirrors rather than a camera itself in order to control the gaze direction. | |
| Batting: | The batting robot can hit a ball anywhere in the strike zone by controlling the arm in response to the position of the ball every 1 ms. We adopt a simple control law without prediction or learning, since all required information is acquired from the high-speed active vision. In addition, the batting robot can control the strike direction by using a planar bat ( Ball Control in High-speed Batting Motion ). | |
| Running: | The high-speed running robot can run with a forward leaning posture thanks to two features: The first is a small and high-speed motion mechanism with high-speed, light-weight actuators, and the second is high-speed visual feedback that recognizes the state and posture of the robot and modifies them in real time. This robot doesn't use ZMP-based control, which is commonly used for biped robots, and runs with an unstable posture in ZMP. We achieved running at 4.2 km/h with 14 cm long legs. | |
| Catching: | We developed two catching robots: One with a fixed hand, and one with a hand connecting with high-speed arm. Both use a high-speed hand that can open and close its fingers 10 times per second. These robots can catch a flying ball by controlling its manipulators in response to movements of the ball measured with high-speed vision. |
Movie
If you want to use the original video, please send an e-mail for copyright permission to contact .
Related Works
Acknowledgment
We use footage of the University of Tokyo Baseball Club during their practice in this video with their permission. We would like to express our deepest gratitude to "The University of Tokyo Baseball Club" and everyone concerned. Ishikawa Group Lab is rooting for the University of Tokyo Baseball Club.



 The throwing robot that can throw a ball precisely into the st- rike zone: It uses
three f- ingers to throw.
The throwing robot that can throw a ball precisely into the st- rike zone: It uses
three f- ingers to throw.

 The batting robot that can hit a ball anywhe- re in the strike zone: It can control
the strike direction.
The batting robot that can hit a ball anywhe- re in the strike zone: It can control
the strike direction.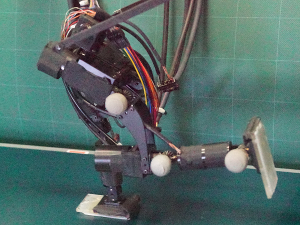 The running robot that can run with a for- ward leaning posture using high-speed vis- ion without ZMP- based control: It runs at 4.2 km/h with 14 cm long legs.
The running robot that can run with a for- ward leaning posture using high-speed vis- ion without ZMP- based control: It runs at 4.2 km/h with 14 cm long legs.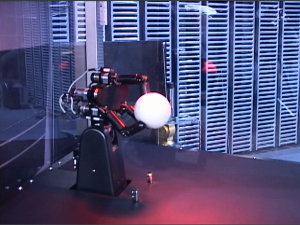 The catching robot that can catch a flying ball using high-speed vision and hand: Both a fixed hand version and a version with a hand connected to an arm exist.
The catching robot that can catch a flying ball using high-speed vision and hand: Both a fixed hand version and a version with a hand connected to an arm exist.