Arterial Simulator for Quantitative Tracheal Endoscopic Image Measurement
Summary
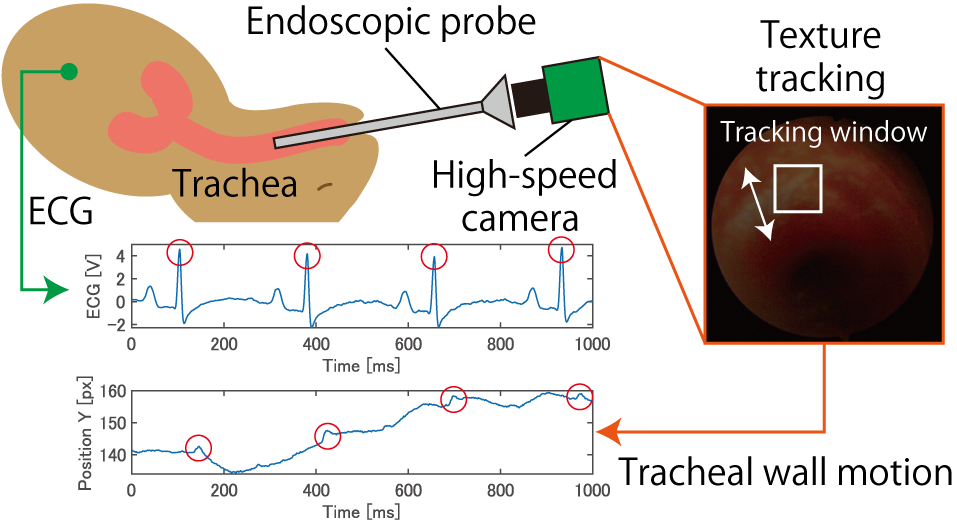
In children, a condition called tracheomalacia occurs where the tracheal cartilage becomes weak, causing the trachea to collapse during inhalation. Currently, diagnosis of tracheomalacia relies solely on qualitative endoscopy. For quantitative diagnosis of tracheomalacia via endoscopy, aiming for equalization of medical care, accurate measurement of respiratory fluctuations is essential. However, spatiotemporal quantification of cardiogenic oscillations on the tracheal wall, which can interfere with respiratory fluctuation measurements, is also required. High-speed endoscopic imaging holds potential for quantifying tracheal and respiratory fluctuations. However, its measurement accuracy and characteristics remain unclear for cardiogenic oscillations within tracheal endoscopic images (Fig. 1), which are thought to include arterial waves. Furthermore, distinguishing between arterial waves and cardiac tissue motion as mechanisms for tracheal wall cardiogenic oscillations is difficult.
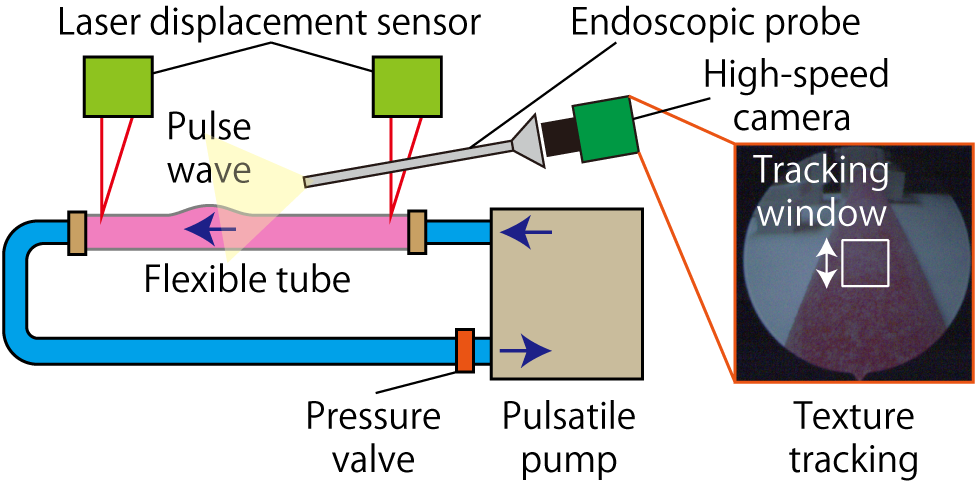
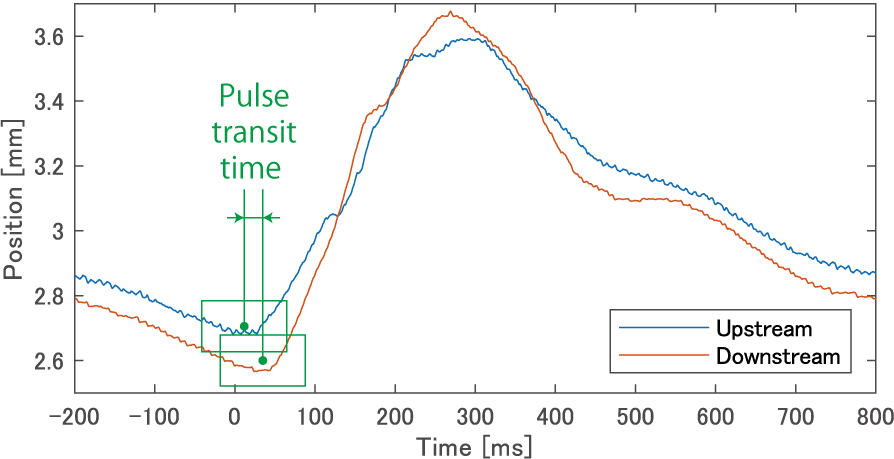
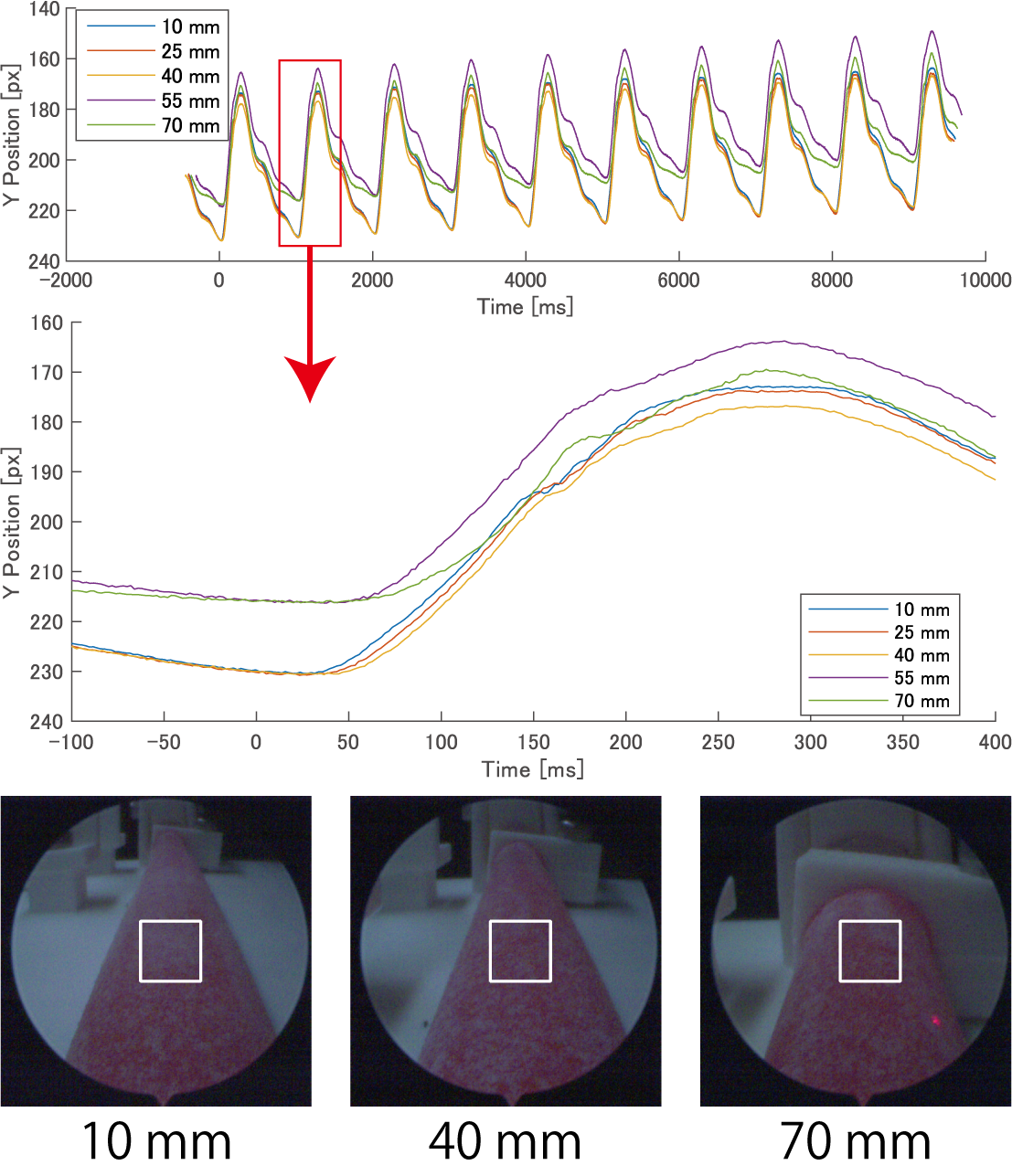
Therefore, this study proposes an arterial simulator (Fig. 2) using a pulsatile pump and an ultra-flexible tube for quantitative endoscopic image measurement. Pulse transit time is measured using laser displacement sensors placed at two points on the tube deformed by the pulse wave (Fig. 3). Furthermore, by adjusting the fluid pressure inside the tube, specific pulse wave velocities can be generated within a certain range. Using this adjusted pulse wave velocity, the accuracy of pulse wave measurement via high-speed endoscopic imaging can be quantified, clarifying its measurement characteristics. We demonstrated that pulse wave measurement via high-speed endoscopic imaging is feasible using the developed arterial simulator (Fig. 4). The development and advancement of quantitative high-speed endoscopic imaging utilizing this simulator is expected to lead to applications in the medical field.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reference
- Tomohiro Sueishi, Makoto Komura, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Arterial Simulator with Configurable Pulse Wave Velocity for Quantitative Tracheal Endoscopic Image Measurement, 2026 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII2026) (Cancun, 2026.1.12)/Proceedings, pp. 21-27 Best Paper Finalist
- Tomohiro Sueishi, Makoto Komura, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-speed Image-based Measurement Method of Tracheal Cardiac-induced Pulse Transit Time, The 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2024) (Orlando, 2024.7.19)/Proceedings, Poster ID.118373



