Effects of Low Video Latency between Visual Information and Physical Sensation in Immersive Environments
Summary
Recently many VR devices using body movement as input have been developed and enable us to intuitively interact with VR space. However, their intrinsic latency before the resulting images are displayed creates a discrepancy between the user's visual information and the physical sensation. In previous study, there are few study about low latency effects in self-projected immersive environment.
Based on a high-speed projector and high-speed camera, we developed a video latency control system to film the user's hand movements and control the latency by 1ms when displaying the video with the minimum system latency 4.3ms. Using this system and mirrors, the immersive environment with latency from user's physical input to the visual feedback was established and enables us to investigate the latency effects in unknown low range (less than 100ms).
We conducted an experiment wherein the subjects performed a pointing task based on Fitts' law to measure the user performance. The experimental results showed that the performance begins to decrease when the latency is over 24ms. Also, in another experiment using a path-steering task, it was revealed that the latency of visual feedback beyond 64.3 ms was associated with reductions in user performance. These results will be applied to determine a standard limit for video latency in self-projected VR devices.
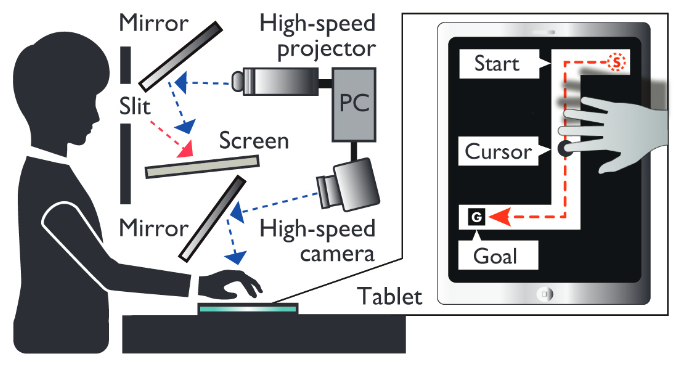
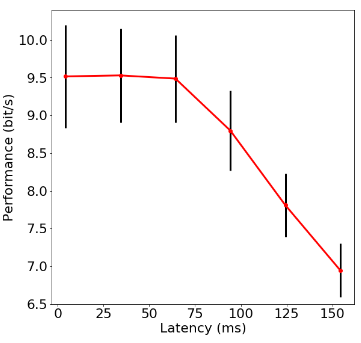
Movie
References
- Himari Tochioka, Tomohiko Hayakawa, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Effects of Video Latency and Target Acceleration on Human Perception Against Physical Sensation in Immersive Environments With Low Visual Feedback Delay, The 26th Annual Conference of the Virtual Reality Society of Japan (VRSJ2021.9.14), 3B2-3.
- Haruka Ikeda, Naoki Fujita, Himari Tochioka, Tomohiko Hayakawa, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Measurements of Refresh Rate in a System with a High-Speed Camera and a High-Speed Projector, IEICE General Conference 2020.
- Naoki Fujita, Haruka Ikeda, Himari Tochioka, Tomohiko Hayakawa, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Effects of Video Latency and Frame Rate on Human Perception in Immersive Environments With Low Latencyof Visual Feedback, IEICE General Conference 2020.
- Himari Tochioka, Haruka Ikeda, Tomohiko Hayakawa, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Effects of Latency in Visual Feedback on Human Performance of Path-Steering Tasks, The 25th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology (VRST2019) (Parramatta, NSW, Australia, 2019.11.12-15), Poster [doi:10.1145/3359996.3364726].
- Himari Tochioka, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Takuya Kadowaki, Haruka Ikeda, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Effects of Video Latency on Human Performance Against Physical Sensation in Immersive Environments With Low Delay of Visual Feedback, The 24th Annual Conference of the Virtual Reality Society of Japan (VRSJ2019), 4C-5.
- Kadowaki, T., Maruyama, M., Hayakawa, T., Matsuzawa, N., Iwasaki, K., & Ishikawa, M.: Effects of Low Video Latency under the Immersive Environment with a Gap between Visual Information and Physical Sensation. Transactions of the Virtual Reality Society of Japan, Vol.24, No.1, pp.23-30, 2019. 22nd VRSJ Outstanding Paper Award
- Kadowaki, T., Maruyama, M., Hayakawa, T., Matsuzawa, N., Iwasaki, K., & Ishikawa, M. (2018, November). Effects of Low Video Latency between Visual Information and Physical Sensation in immersive environments. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology (p. 84). ACM.
- Kadowaki, T., Maruyama, M., Hayakawa, T., Matsuzawa, N., Iwasaki, K., & Ishikawa, M.: Effects of Low Video Latency under performance the Immersive Environment with a Gap between Visual Information and Physical Sensation. In Proceedings of 23th the Virtual Reality Society of Japan (VRSJ2018) (Sendai, 2018.9.19), 12B-1.



